Light travels away from a light source until it. Does it have a frequency like sound.
There are many types of light of which the visible spectrum is a small part.

How does light travel explanation. When light is not in a vacuum it travels more slowly than its maximum speed of light. Light travels in waves. Light travels in waves of frequency and as particles of matter.
This means that light can travel through a vacuuma completely airless space. Light is a kind of energy. How does light travel.
How does light travel. But why does light make this journey at all. The only possible explanation for this pattern of interference was that the light beams were in fact behaving as waves.
But unlike sound waves or water waves it does not need any matter or material to carry its energy along. Going through partly clear objects can slow light down by a very small amount. Lesson for kids.
Is it a single color or many colors mixed together. The speed at which light moves does not depend on its energy. Put it another way light takes roughly twice as long to get from the sun to earth as it does to make a cup of coffee.
Light travels as a wave. But how exactly does light move so quickly. In this lesson well investigate the.
Visible light is the light that can be seen with the naked eye. This speed variation causes light to bend at the interface of two media a phenomenon called refraction. You might think scientists know all the answers but light continues to surprise them.
Does light travel as a wave a ray or a stream of particles. It is one type of electromagnetic radiation which results from the vibrations of electric and magnetic fields. Light travels slower in a medium than it does in a vacuum and the speed is proportional to the density of the medium.
Light rays cannot bend to go around something. Light is produced from light sources such as a lamp a candle or the sun. Light travels at 186000 miles 300000 km per second so the light youre seeing now was still tucked away in the sun about eight minutes ago.
And what are some of the common properties of light such as absorption reflection refraction and diffraction. The slowest light ever recorded moved at 39 mph. Does it travel in waves like sound or in little particles.
An explanation of where light comes from and how shadows are created. Watch out this video to understand these terms in detail. The light rays are either reflected absorbed or refracted.
Thus this experiment dispelled the notion that light consisted of.
 1 Nature Of Light 2 Nature Of Light What Am I Waves Particles
1 Nature Of Light 2 Nature Of Light What Am I Waves Particles
 Science Video For Kids How Does Light Travel Youtube
Science Video For Kids How Does Light Travel Youtube
 How Fast Does Light Travel In Water Vs Air Refraction Experiment
How Fast Does Light Travel In Water Vs Air Refraction Experiment
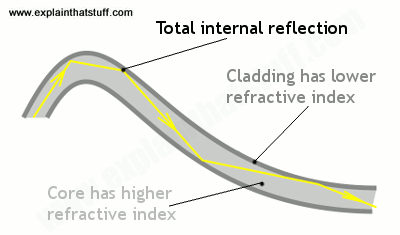 How Does Fiber Optics Work Explain That Stuff
How Does Fiber Optics Work Explain That Stuff
 Argument And Explanation Development In Secondary Science Day 1
Argument And Explanation Development In Secondary Science Day 1
 Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
 What Is Light How Fast Does Light Travel Socratic
What Is Light How Fast Does Light Travel Socratic
 Readings Light Refraction Of Light
Readings Light Refraction Of Light
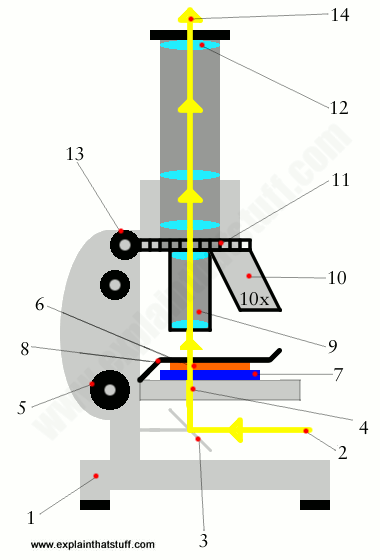 How Does A Microscope Work Explain That Stuff
How Does A Microscope Work Explain That Stuff
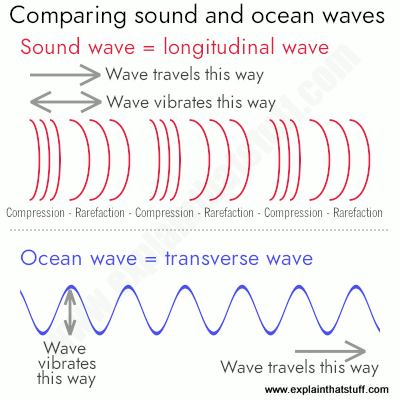 Sound The Science Of Waves How They Travel How We Use Them
Sound The Science Of Waves How They Travel How We Use Them
 Faster Than Light Movement And Time Travel Simple Explanation
Faster Than Light Movement And Time Travel Simple Explanation
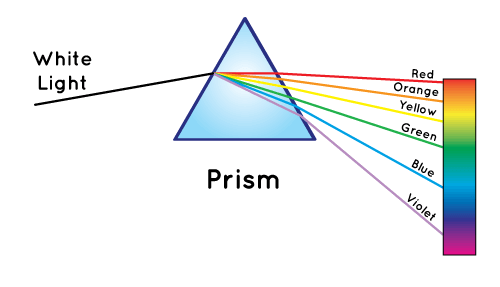 Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
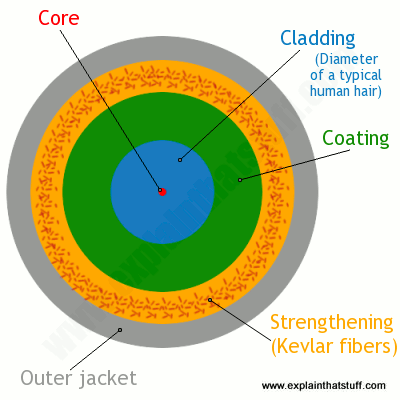 How Does Fiber Optics Work Explain That Stuff
How Does Fiber Optics Work Explain That Stuff
A Brief History Of Light Quantum Hertz
 Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
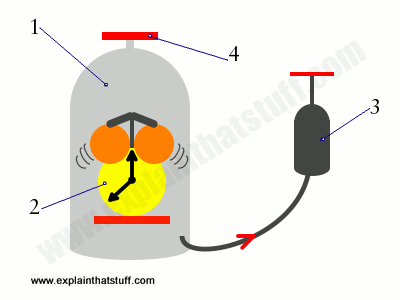 Sound The Science Of Waves How They Travel How We Use Them
Sound The Science Of Waves How They Travel How We Use Them
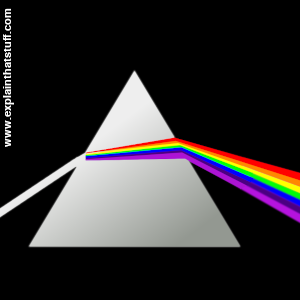 Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
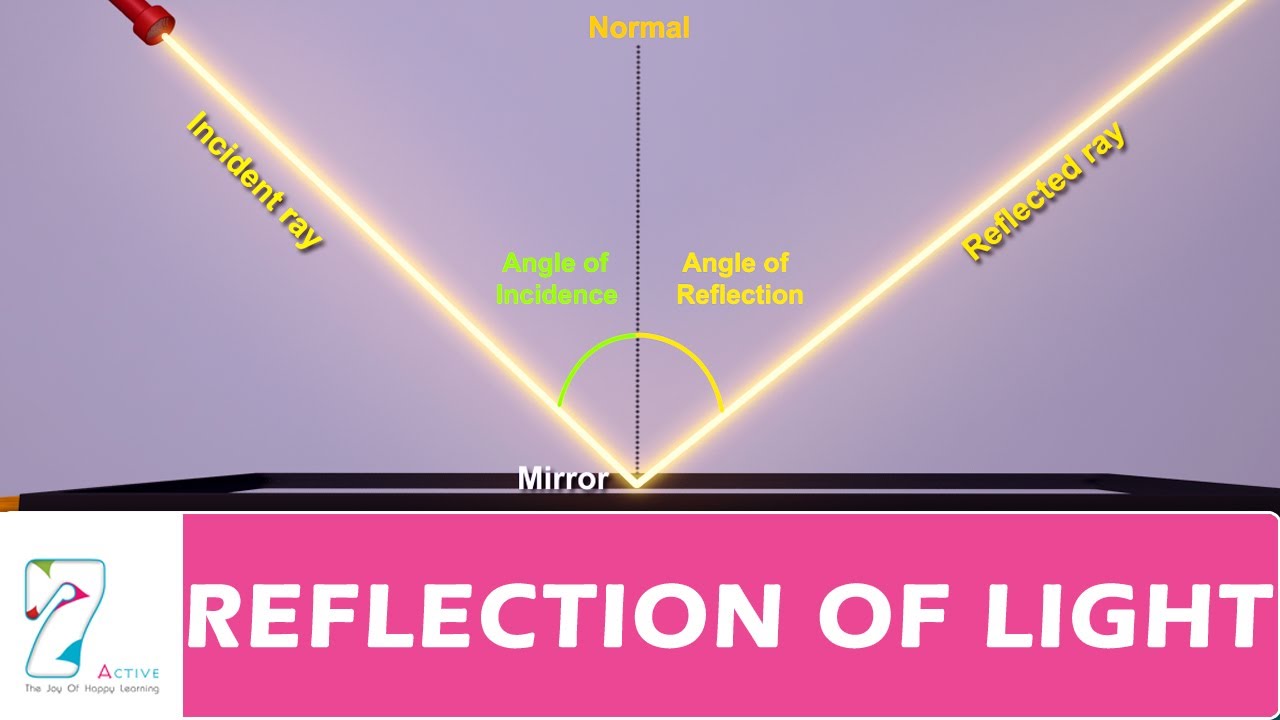
 How Mirrors Work Explain That Stuff
How Mirrors Work Explain That Stuff
 California How Far Does Light Travel In One Second
California How Far Does Light Travel In One Second
 What Is Light How Fast Does Light Travel Socratic
What Is Light How Fast Does Light Travel Socratic

 How Fast Does Light Travel In Water Vs Air Refraction Experiment
How Fast Does Light Travel In Water Vs Air Refraction Experiment
 Electromagnetic Spectrum Types Of Electromagnetic Waves Compared
Electromagnetic Spectrum Types Of Electromagnetic Waves Compared
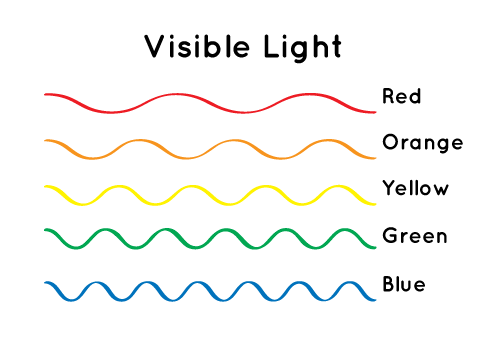
 Visible Light Science Mission Directorate
Visible Light Science Mission Directorate
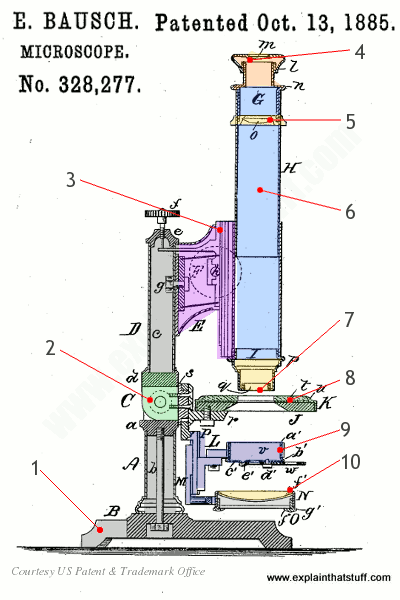 How Does A Microscope Work Explain That Stuff
How Does A Microscope Work Explain That Stuff
 Light Travels In A Straight Line School Science Project Youtube
Light Travels In A Straight Line School Science Project Youtube
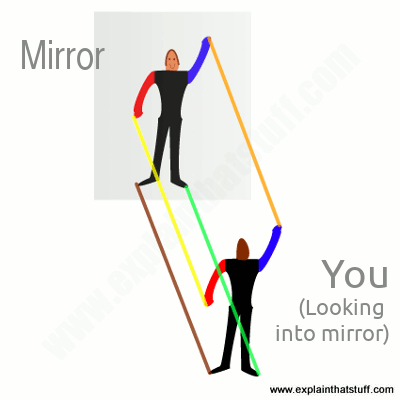 How Mirrors Work Explain That Stuff
How Mirrors Work Explain That Stuff
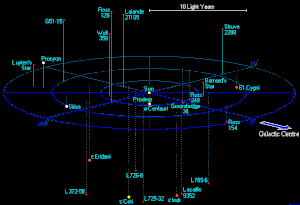
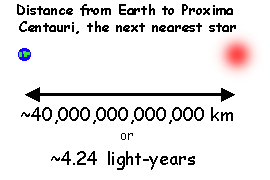 What Is A Light Year And How Is It Used
What Is A Light Year And How Is It Used
 How Do Binoculars Work Explain That Stuff
How Do Binoculars Work Explain That Stuff
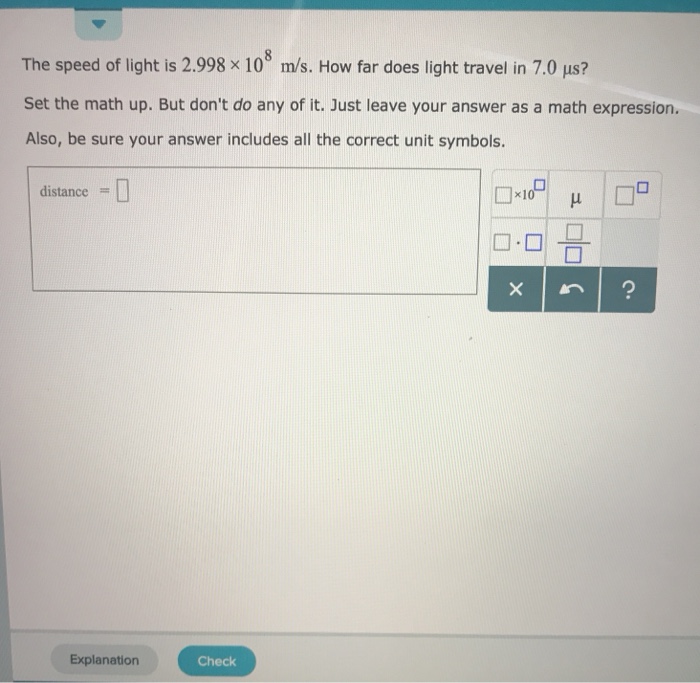
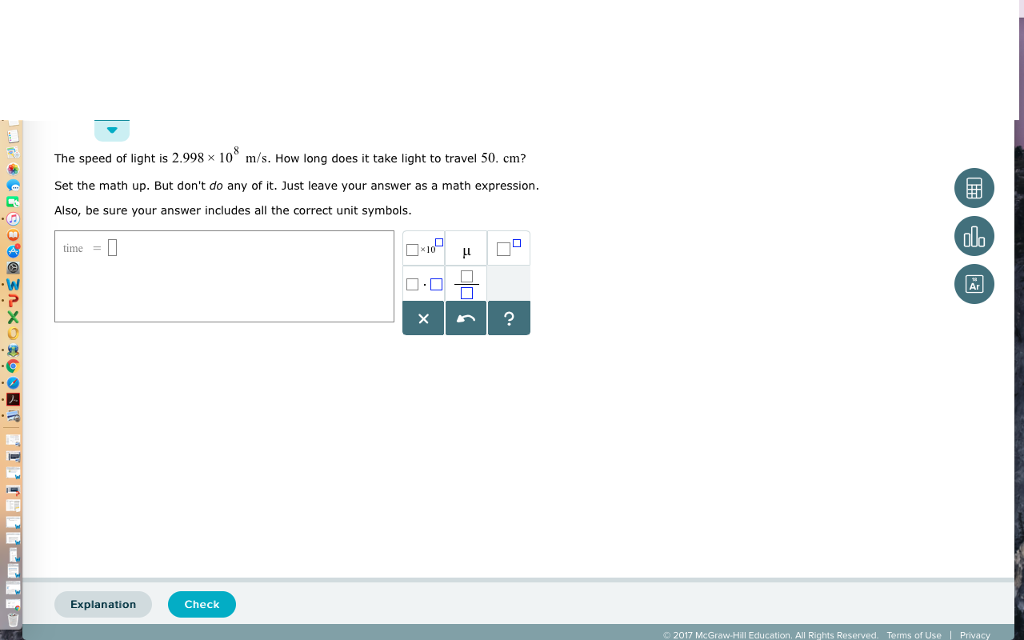 Solved The Speed Of Light Is 2 998 10 M S How Long Do
Solved The Speed Of Light Is 2 998 10 M S How Long Do
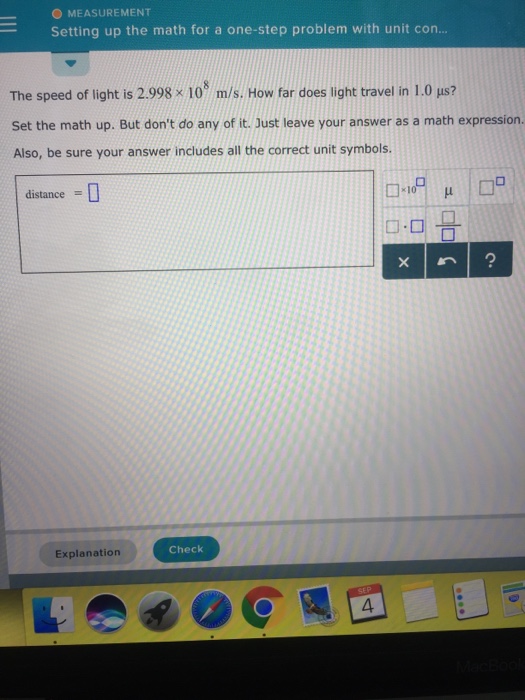
 Can Faster Than Light Particles Explain Dark Matter Dark Cosmos
Can Faster Than Light Particles Explain Dark Matter Dark Cosmos
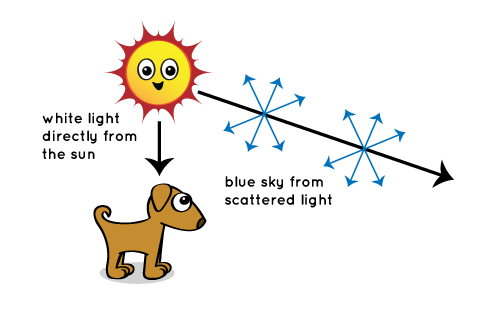 Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
 Why Is The Speed Of Light In A Vacuum Constant The
Why Is The Speed Of Light In A Vacuum Constant The
 Canon Canon Technology Canon Science Lab Light Is It A Wave Or
Canon Canon Technology Canon Science Lab Light Is It A Wave Or
 How Fast Does Light Travel In Water Vs Air Refraction Experiment
How Fast Does Light Travel In Water Vs Air Refraction Experiment
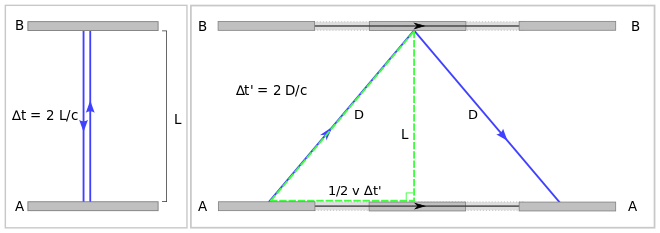
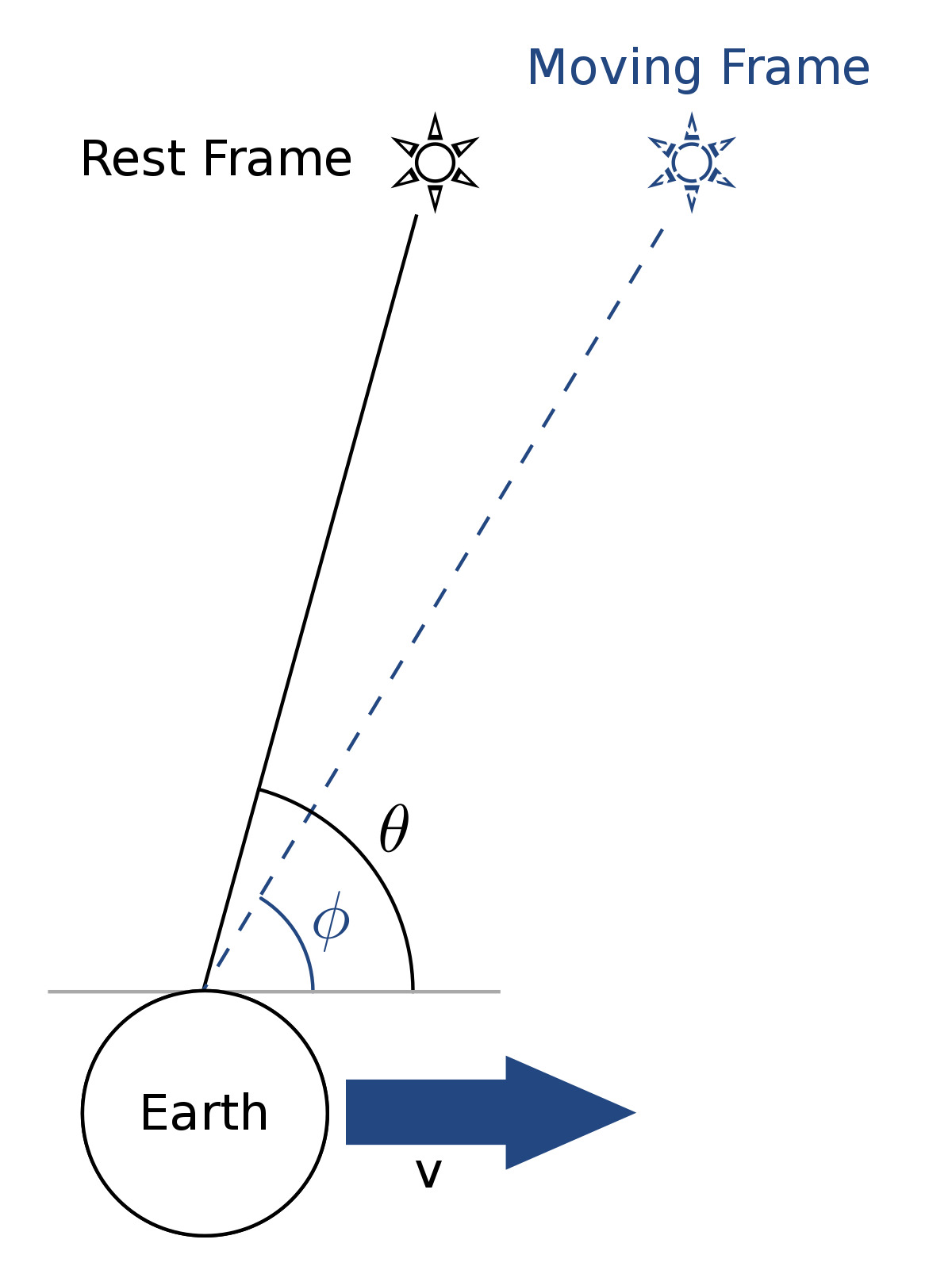
 Explaining Gravitational Time Dilation Geometrically
Explaining Gravitational Time Dilation Geometrically
 Light And How We See Gold Guided Reading Pack Classroom Secrets
Light And How We See Gold Guided Reading Pack Classroom Secrets
How Far Is A Light Year Astronomy Essentials Earthsky
What Is A Light Year Find Out Space Earthsky
 Why Can T Anything Go Faster Than The Speed Of Light
Why Can T Anything Go Faster Than The Speed Of Light
 Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
Refraction Of Light As It Passes From More Dense To Less Dense Mediums
 Canon Canon Technology Canon Science Lab Light Is It A Wave Or
Canon Canon Technology Canon Science Lab Light Is It A Wave Or
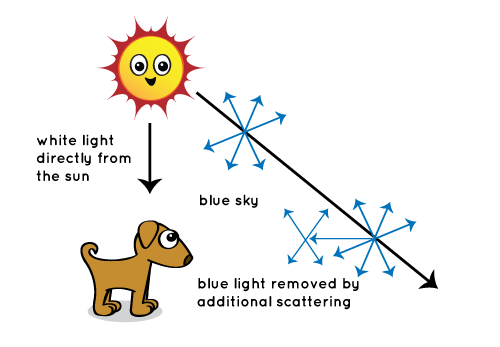 Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
Why Is The Sky Blue Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
What Is Refraction Causes Of Color
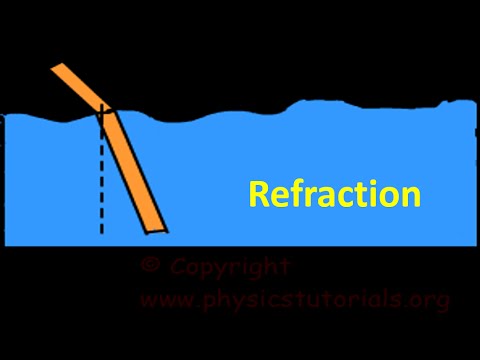 What Is Refraction Of Light Optics For Kids Youtube
What Is Refraction Of Light Optics For Kids Youtube
 Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
Light Science For Kids A Simple Introduction To Optics
Oregon Does Light Travel Faster Than Sound
 Refracting Telescopes Las Cumbres Observatory
Refracting Telescopes Las Cumbres Observatory
 How Long Does It Take Sunlight To Reach The Earth
How Long Does It Take Sunlight To Reach The Earth
Bbc Science How Do Telescopes Let Us See So Far Into Space
 How Does Fiber Optics Work Explain That Stuff
How Does Fiber Optics Work Explain That Stuff
Bbc Science How Do Telescopes Let Us See So Far Into Space
 Argument And Explanation Development In Secondary Science Day 1
Argument And Explanation Development In Secondary Science Day 1
E Mc 2 An Explanation Of The Basics And Units
Q A How Do Telescopes Work Department Of Physics University
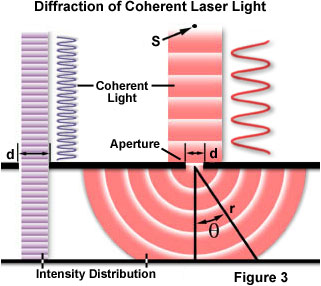 The Physics Of Light And Color Diffraction Of Light
The Physics Of Light And Color Diffraction Of Light
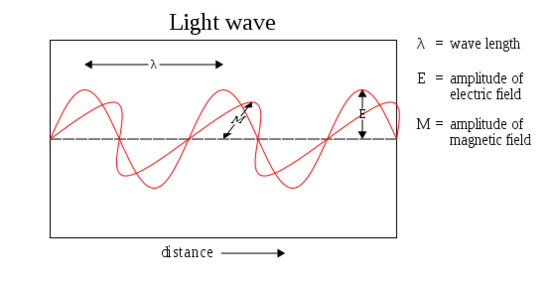 Light Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum And
Light Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum And
 The Speed Of Light And The Index Of Refraction
The Speed Of Light And The Index Of Refraction
 Is Light A Wave Or A Particle Wired
Is Light A Wave Or A Particle Wired
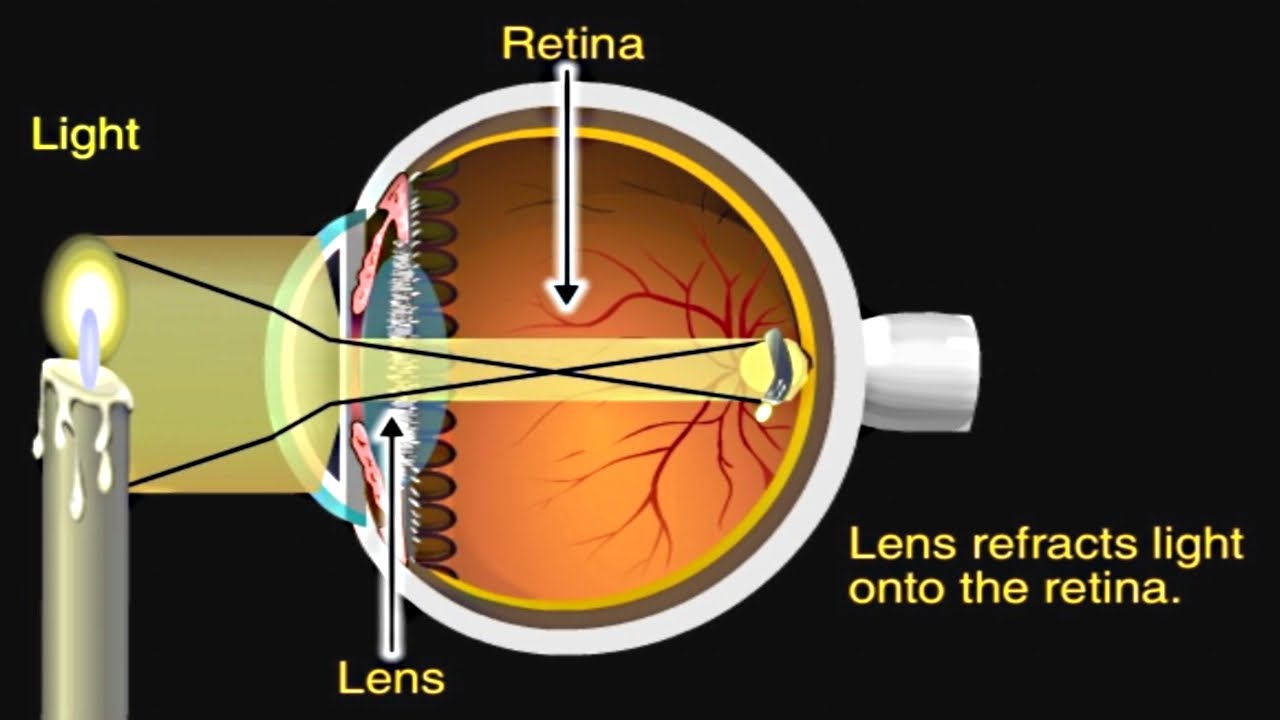 How The Eye Works Animation How Do We See Video Nearsighted
How The Eye Works Animation How Do We See Video Nearsighted
 Refraction Of Light Science Learning Hub
Refraction Of Light Science Learning Hub
 Light We Have Observed Light 1 Travels In Straight Lines
Light We Have Observed Light 1 Travels In Straight Lines













Post a Comment